Radiation Therapy Side Effects
The side effects of radiation therapy depend on the type of radiation therapy youre having. In general, the side effects tend to develop as treatment goes on and may be more troubling toward the end of treatment. Overall, the most common side effects are redness, swelling, and skin peeling in the area being treated. Read more about radiation therapy side effects.
Vitamins To Avoid During Radiation Therapy
Your radiation oncologist may tell you to avoid taking certain antioxidant vitamin supplements, such as vitamins C, A, D, and E, while you’re having radiation therapy. These vitamins might interfere with radiation’s ability to destroy cancer cells.This is because radiation works in part by creating free radicals highly energized molecules that damage cancer cells. Free radicals in the environment can damage all cells, but in the case of radiation treatment they are focused on the cancer cells. Antioxidants help keep free radicals from forming or neutralize them if they do form.
Because of the potential conflict between the goal of radiation therapy and the goal of antioxidants , it makes sense to stop taking any antioxidant supplements during radiation therapy. When radiation is finished, you can resume taking your supplements.
Throughout your treatment, do your best to eat a well-balanced diet that contains all of the vitamins you need. Vitamins that come naturally from food are unlikely to interfere with treatment.
Adjuvant Radiation In Breast
WBI is given following lumpectomy to eliminate residual microscopic disease that may remain in the breast even when negative margins are obtained. Holland et al, in pathologic studies of mastectomy specimens in 282 patients with clinical and mammographically unifocal breast cancers, found additional tumor foci within 2 cm of the index tumor in 56 cases and > 2 cm from the index cancer in 121 cases. The delivery of adjuvant radiation following lumpectomy decreases local failure rates by about 50% and increases breast cancer-specific survival.â, The Early Breast Cancer Trialistsâ Collaborative Group meta-analysis of 17 randomized trials including 10,801 women undergoing BCT demonstrated a reduction in the risk of any recurrence at 10 years from 35% to 19.3% and a 15-year absolute reduction in the risk of death from breast cancer of 3.8% with radiation. Investigators extrapolate that for every 4 recurrences that are prevented at 10 years, there is a corresponding avoidance of 1 breast cancer death at 15 years.
Also Check: Stage 4 Breast Cancer In Lungs
Radiation Therapy For Breast Cancer In Men
Some men with breast cancer will need radiation, often in addition to other treatments. The recommendations for radiation therapy in men with breast cancer is largely taken from those for female breast cancer because not enough studies have been done in men. The need for radiation depends on what type of surgery you had or whether your cancer has spread to the lymph nodes or somewhere else in your body. Tumors that are large or involve the skin might also need radiation. You could have just one type of radiation, or a combination of different types.
Radiation therapy is treatment with high-energy rays or particles that destroy cancer cells. The most common type of radiation therapy for men with breast cancer is called external beam radiation. A machine focuses the radiation on the area affected by the cancer.
How Is Radiation Therapy Given
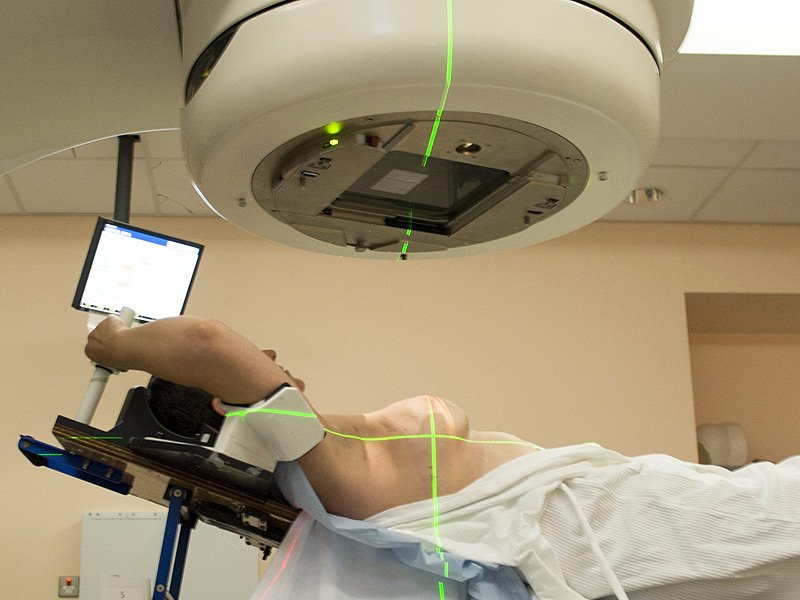
Radiation therapy can be given in 3 ways:
- External radiation : uses a machine that directs high-energy rays from outside the body into the tumor. Its done during outpatient visits to a hospital or treatment center. It’s usually given over many weeks and sometimes will be given twice a day for several weeks. A person receiving external radiation is not radioactive and does not have to follow special safety precautions at home.
- Internal radiation: Internal radiation is also called brachytherapy. A radioactive source is put inside the body into or near the tumor. With some types of brachytherapy, radiation might be placed and left in the body to work. Sometimes it is placed in the body for a period of time and then removed. This is decided based on the type of cancer. Special safety precautions are needed for this type of radiation for a period of time. But it’s important to know if the internal radiation is left in the body, after a while it eventually is no longer radioactive.
- Systemic radiation: Radioactive drugs given by mouth or put into a vein are used to treat certain types of cancer. These drugs then travel throughout the body. You might have to follow special precautions at home for a period of time after these drugs are given.
Don’t Miss: Can You Live 10 Years With Metastatic Breast Cancer
What Are Possible Side Effects Of Radiation Therapy
There are usually no immediate side effects from each radiation treatment given to the breast. Patients do not develop nausea or hair loss on the head from radiation therapy to the breast.
Most patients develop mild fatigue that builds up gradually over the course of therapy. This slowly goes away one to two months following the radiation therapy. Most patients develop dull aches or sharp shooting pains in the breast that may last for a few seconds or minutes. It is rare for patients to need any medication for this. The most common side effect needing attention is skin reaction. Most patients develop reddening, dryness anditching of the skin after a few weeks. Some patients develop substantial irritation.
Skin care recommendations include:
- Keeping the skin clean using gentle soap and warm but not hot water
- Avoiding extreme temperatures while bathing
- Avoiding trauma to the skin and sun exposure
- Avoiding shaving the treatment area with a razor blade
- Avoiding use of perfumes, cosmetics, after-shave or deodorants in the treatment area
- Using only recommended unscented creams or lotions after daily treatment
What To Expect During Internal Radiation Therapy
For internal radiation therapy, the radiation is directed from inside the body. The radiation therapist places a small thin hollow tube directly into the breast where the tumor used to be. Radioactive seeds or pellets are then put into the catheter for short periods of time each day. They are then removed when the treatment is over. Internal radiation may be done along with or instead of EBRT. Some types of internal radiation require a balloon-type device to be inserted into your breast . The device is put into the hole the surgeon created when removing your cancer. This balloon device stays in place for about 7 to 10 days. Radiation is put into the balloon twice a day for a total of 5 sessions. Then the balloon is deflated and removed.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Prognosis For Stage 4 Breast Cancer
Does Radiation Therapy Affect Pregnancy Or Fertility
Females: Its important not to become pregnant while getting radiation it can harm the growing baby. If theres a chance you might become pregnant, be sure to talk to your doctor about birth control options.
If you are or might be pregnant, let your doctor know right away.
If the area getting radiation in your body includes the ovaries, it is possible that the dose of radiation can cause the ovaries to no longer work , and that you would be unable to have children. it is important to know the risk of this possibility in advance of receiving radiation therapy. If you are thinking about radiation therapy that will affect the ovaries, talk to your doctor about how this might affect having children in the future.
Males: Not much is known about radiations effect on the children conceived by men while getting radiation therapy. Because of this, doctors often advise men to not get a woman pregnant during and for some weeks after treatment. Talk to your doctor to find out more about this.
Learn more in How Cancer and Cancer Treatment Can Affect Fertility.
To Treat Symptoms Caused By Advanced Cancer
Sometimes cancer has spread too much to be cured. But some of these tumors can still be treated to make them smaller so that the person can feel better. Radiation might help relieve problems like pain, trouble swallowing or breathing, or bowel blockages that can be caused by advanced cancer. This is called palliative radiation.
You May Like: Is Breast Cancer Curable
Are Some Therapies More Effective Based On Stage
The type of radiation treatment you get depends on the stage of breast cancer. People with early to stage 3 breast cancer will benefit most from radiation treatment. Radiation can also help ease side effects in people with advanced breast cancer.
External whole breast radiation works best:
- for early stage to stage 3 breast cancer
- for tumors that are an inch or smaller
- if the cancer is in one spot
- if you had breast-saving surgery or a mastectomy
External beam radiation can also help treat side effects of advanced breast cancer.
Internal radiation works best:
- for early stage breast cancer
- if the cancer is in one spot
- if you had breast-saving surgery or a mastectomy
Sometimes, a person with advanced breast cancer will have internal radiation.
Intraoperative radiation works best:
- during early stage breast cancer
- when the tumor is too close to healthy tissue for external radiation to be possible
Not everyone can have intraoperative radiation or internal beam radiation. Whether you can have these procedures depends on:
- size and location of the tumor
- size of your breast
What Kind Of Treatment Follow
The major goal of follow-up is, if possible, to detect and treat recurrences in the irradiated breast or lymph nodes and new cancers developing later in either breast before they can spread to other parts of the body. Theroutine use of bone scans, chest x-rays, blood tests and other tests to detect the possible spread to other organs in patients without symptoms does not appear to be useful. Your physician will determine a follow-upschedule for you. This may include a physical exam every few months for the first several years after treatment and then every six to 12 months or so after that. Annual follow-up mammograms are an important part of your care. If symptoms or clinical circumstances suggest a recurrence, diagnostic tests such as blood tests, ultrasound,computed tomography , magnetic resonance imaging , chest x-ray , or bone scan may be needed.
Read Also: Can Cancer Come Back In The Same Breast
What Can I Expect From My Treatment
When you arrive, please check in at the desk. Each treatment should only last 10 to 15 minutes. You can change your clothes in the dressing room and then wait in the lounge to be called.
During each treatment session, you will lay on a table while the technician uses the marks on your skin to locate and treat the field. It is important to be still while getting the radiation, although you should continue to breathe normally.
Preparing For External Beam Radiation Therapy
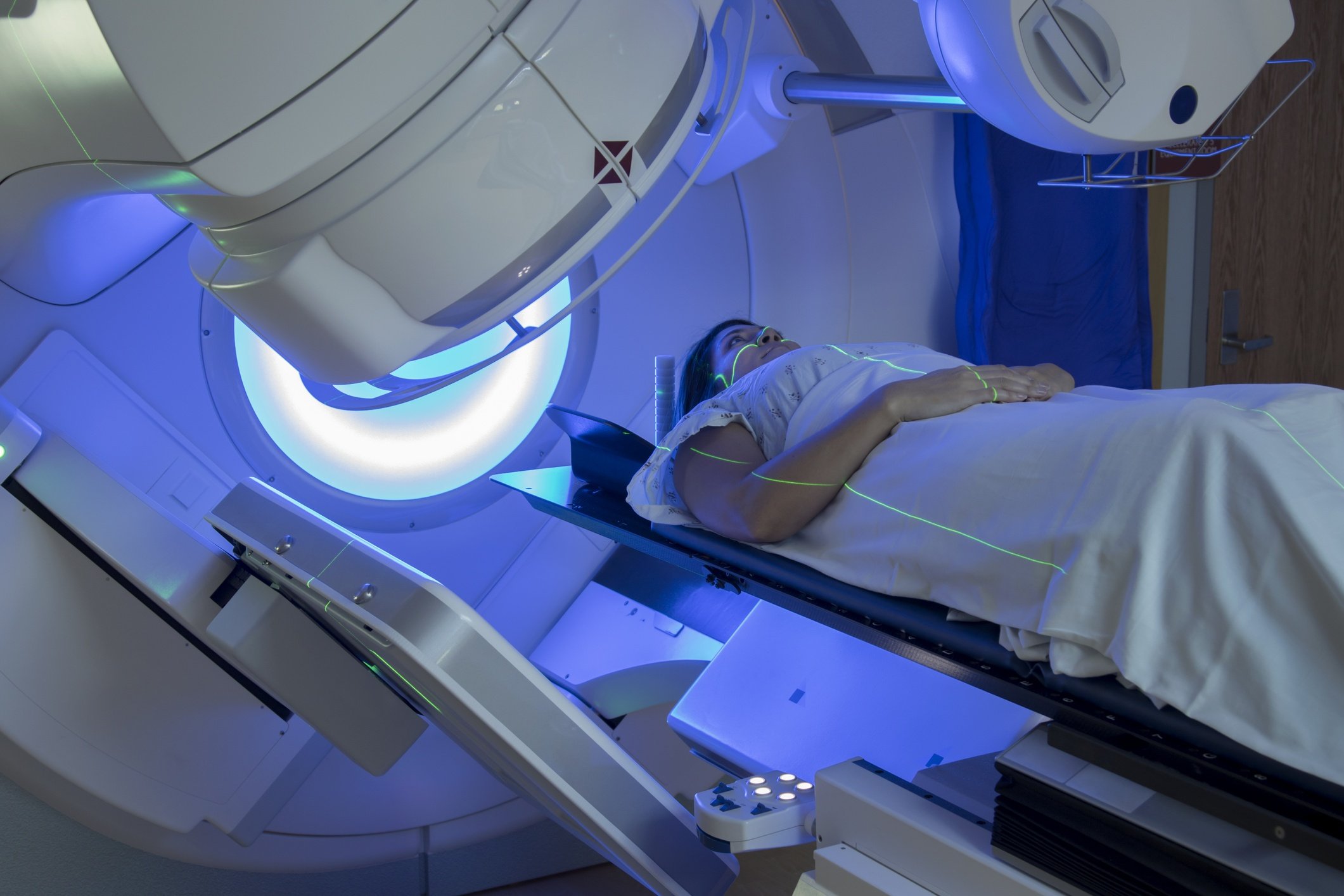
Before your treatment starts, the radiation team will carefully figure out the correct angles for aiming the radiation beams and the proper dose of radiation. They will make some ink marks or small tattoos on your skin to focus the radiation on the right area. Ask your health care team if the marks they use will be permanent.
External radiation therapy is much like getting an x-ray, but the radiation is stronger. The procedure itself is painless. Each treatment lasts only a few minutes, but the setup timegetting you into place for treatmentusually takes longer.
Recommended Reading: Hr Positive Her2 Negative Metastatic Breast Cancer
Types Of Radiation For Breast Cancer
External-beam radiation therapy is the most common form of radiation treatment for breast cancer. In this approach, a machine called a linear accelerator, or LINAC, produces radiation. The radiation is delivered as precisely targeted x-ray beams.
At MSK, we deliver external-beam radiation therapy in a variety of ways. These approaches are designed to tailor the radiation treatments as much as possible to the exact size and location of your cancer, specifically aiming at tumor cells while avoiding side effects.
We also offer internal radiation therapy in the form of brachytherapy. Brachytherapy is generally reserved for women receiving partial-breast irradiation after lumpectomy.
Learn more about the techniques our breast cancer radiation team frequently recommends.
In this method, patients lie on their stomach . Radiation is directed to the affected breast as it hangs through an opening in the treatment table. This approach may reduce radiation exposure to nearby vital organs, such as the heart and lungs. Prone breast radiation has been shown to reduce radiation burn on the skin. Research has also shown that this therapy is especially useful for women with large breasts.
In this approach, our experienced radiation therapists guide women with cancer in the left breast through a breathing technique called deep inspiration breath hold . It minimizes the risk of injury to the heart.
Expectations And What To Avoid
Radiation therapy should not cause pain or discomfort during the procedure. However, minor side effects are common in the days or weeks afterward. Before beginning radiation therapy, an individual should schedule a consultation with their doctor to work out the details.
People should also take some precautions while they are receiving radiation therapy. For example, they should avoid direct sun exposure by using sunscreen and covering up areas of bare skin when outside.
Also, taking antioxidant supplements, such as vitamins A, C, D, and E, can interfere with radiation therapys effectiveness. People should, therefore, focus on eating a well-balanced diet so that their body can absorb the nutrients and vitamins it needs from food.
Read Also: How Do Doctors Treat Breast Cancer
Does Radiation Therapy Cause Cancer
It has long been known that radiation therapy can slightly raise the risk of getting another cancer. Its one of the possible side effects of treatment that doctors have to think about when they weigh the benefits and risks of each treatment. For the most part, the risk of a second cancer from these treatments is small and is outweighed by the benefit of treating the cancer, but the risk is not zero. This is one of the many reasons each case is different and each person must be part of deciding which kind of treatment is right for them. The risk is different depending on where the radiation treatment will be in the body.
If your cancer care team recommends radiation treatment, its because they believe that the benefits youll get from it will outweigh the possible side effects. Still, this is your decision to make. Knowing as much as you can about the possible benefits and risks can help you be sure that radiation therapy is best for you.
Having Radiotherapy For Breast Cancer
Radiotherapy uses high energy x-rays to treat cancer cells.
You might have external beam radiotherapy after breast surgery to lower the risk of the cancer coming back.
You have your treatment in the hospital radiotherapy department. You usually have it from Monday to Friday with a break at the weekend. The treatment is usually over 3 weeks. Each daily treatment is called a fraction.
There are studies looking at giving different doses of radiotherapy over a shorter time. Doctors want to try to reduce the risk of side effects. How often you have treatment may change in the future if the results show that a different treatment is better.
You need to travel to the hospital each time you have treatment. Some hospitals have rooms nearby where you can stay if you have a long way to travel.
You go to the radiotherapy department from your ward if you are staying in the hospital.
Don’t Miss: What Is Stage 3a Breast Cancer
Adjuvant Medical Therapies For Breast Cancer
Following surgical resection of the primary breast cancer, patients often receive adjuvant systemic therapy with the goal of eradicating clinically and radiographically occult micrometastatic disease that may develop into frank metastatic disease if left untreated. Selection of adjuvant systemic therapies is based on risk stratification of the patient. Two factors affect risk: disease burden and disease biology as determined by HR and HER2 status, and genomic assays. While patients with triple negative and HER2 positive cancers are generally considered to be high risk, there is considerable biologic diversity among those with HR positive, HER2 negative cancers. Based on trials demonstrating a small but statistically significant benefit for treatment of HR positive, HER2 negative, node-negative breast cancers with chemotherapy in addition to endocrine therapy, chemotherapy has been standard for healthy women in this group. Commercially available genomic assays including Oncotype DX and Mammaprint examine cancer-related genes in tumor-derived DNA to determine risk of recurrence and potential chemotherapy benefit. These commercially available tests have given clinicians more clarity on which patients should receive chemotherapy.
Radiation Therapy And Sun Exposure
During radiation treatment, its best to keep the treated area completely out of the sun. This can be especially difficult if youre having radiation therapy in areas or seasons with warmer weather. To help avoid sun exposure:
- Wear clothing or a bathing suit with a high neckline, or wear a rash guard top.
- Try to keep the area covered whenever you go outside. An oversized cotton shirt works well and allows air to circulate around the treated area.
- Avoid chlorine, which is very drying and can make any skin reactions youre having worse. Chlorine is used to disinfect most pools and hot tubs.
- If you do want to swim in a pool, you might want to spread petroleum jelly on the treated area to keep the chlorine away from your skin.
After your radiation treatment is completed, the treated skin may be more sensitive to the sun than it was in the past, so you might need to take extra protective steps when you go out in the sun:
- Use a sunblock rated 30 SPF or higher on the area that was treated.
- Apply the sunblock 30 minutes before you go out in the sun.
- Reapply the sunblock every few hours, as well as when you get out of the water.
Written by: Jamie DePolo, senior editor
This content was developed with contributions from the following experts:
Chirag Shah, M.D., breast radiation oncologist, director of breast radiation oncology and clinical research in radiation oncology at the Cleveland Clinic in Cleveland, Ohio
References
Read Also: How To Cure Breast Cancer With Baking Soda